If you’ve ever experienced anxiety, panic attacks, or insomnia, you know how debilitating these conditions can be. They can disrupt your daily routine, hinder your productivity, and affect your overall well-being. Fortunately, there are medications available that can help alleviate these symptoms and improve your quality of life. Ativan, also known as lorazepam, is one of the most commonly prescribed drugs for anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at Ativan, its uses, dosage, side effects, and precautions.
What is Ativan?
Ativan is a benzodiazepine medication that belongs to the class of minor tranquilizers. It works by enhancing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain that regulate mood, anxiety, and sleep. Ativan is available in various forms, including oral tablets, liquid concentrate, and intravenous (IV) injection. The drug is a Schedule IV controlled substance, which means it has a low potential for abuse and dependence compared to other benzodiazepines.

Uses of Ativan
Ativan is primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. It can also be used as a short-term treatment for insomnia, agitation, and muscle spasms. Ativan is sometimes used as an adjunctive therapy for depression, especially when other medications have failed to produce significant improvement.
Ativan Dosage
The dosage of Ativan depends on the condition being treated, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s age, weight, and medical history. The drug is usually started at a low dose and gradually increased as needed. The typical starting dose for anxiety is 0.5 mg to 1 mg taken two to three times a day, while the starting dose for insomnia is 2 mg to 4 mg taken at bedtime. The maximum daily dose of Ativan should not exceed 10 mg.
Ativan Prescription
Ativan is a prescription medication that should only be taken under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and not to exceed the recommended duration of treatment. Abruptly stopping Ativan can cause withdrawal symptoms, including rebound anxiety, insomnia, tremors, and seizures. Long-term use of Ativan can also lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
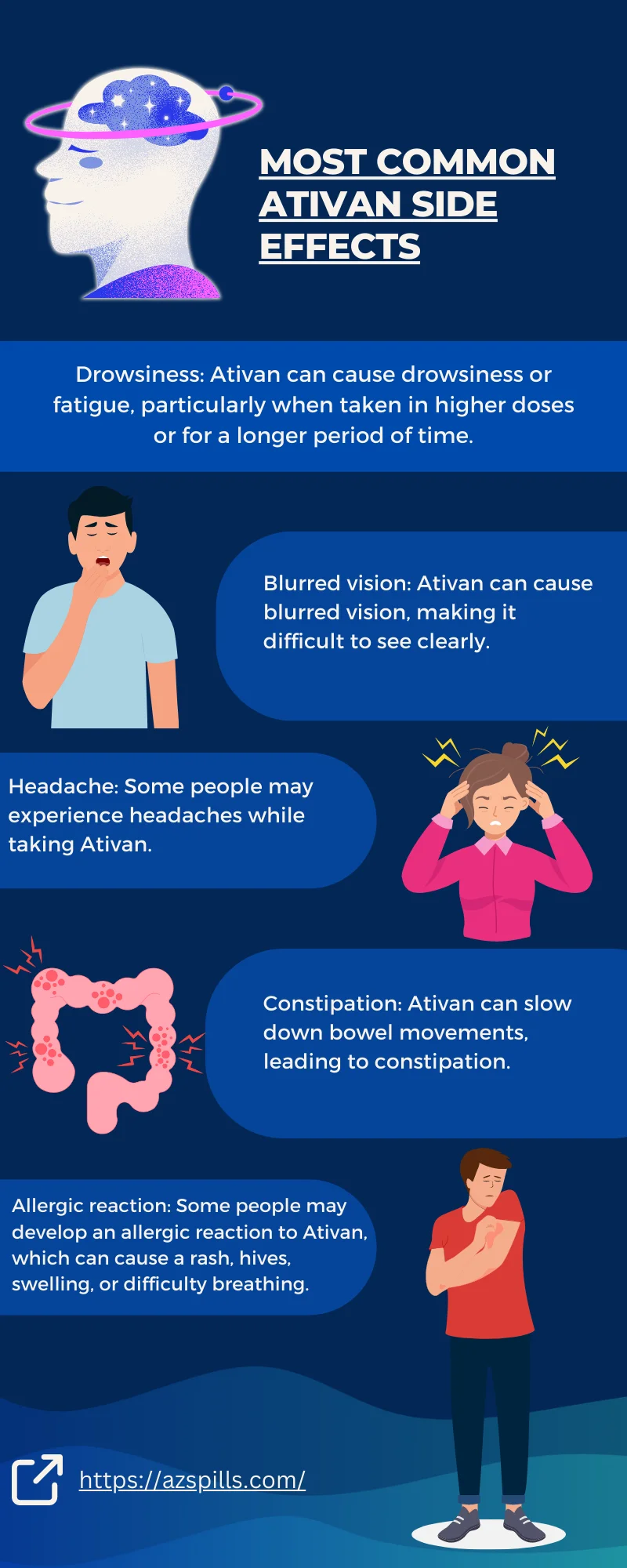
Ativan Side Effects
Side effects of Ativan can vary from person to person. While some people may not experience any side effects, others may experience one or more of the following:
- Drowsiness: Ativan can cause drowsiness or fatigue, particularly when taken in higher doses or for a longer period of time.
- Dizziness: Some people may experience dizziness or lightheadedness while taking Ativan.
- Impaired coordination: Ativan can affect coordination and balance, making it difficult to perform certain activities.
- Blurred vision: Ativan can cause blurred vision, making it difficult to see clearly.
- Headache: Some people may experience headaches while taking Ativan.
- Nausea and vomiting: Ativan can cause nausea and vomiting, particularly when taken on an empty stomach.
- Constipation: Ativan can slow down bowel movements, leading to constipation.
- Memory impairment: At higher doses or with long-term use, Ativan can cause memory impairment or difficulty recalling information.
- Confusion: Some people may experience confusion or disorientation while taking Ativan.
- Respiratory depression: Ativan can slow down breathing and cause respiratory depression, particularly when taken in higher doses.
- Allergic reaction: Some people may develop an allergic reaction to Ativan, which can cause a rash, hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
It is important to note that while some of these side effects may be common, others may be more serious and require immediate medical attention. If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking Ativan, speak with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Ativan Over the Counter
Ativan is not available over the counter and can only be obtained with a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. Buying Ativan from unauthorized sources or without a prescription is illegal and can pose serious health risks. Misusing Ativan can lead to addiction, overdose, and other adverse effects.
Ativan for Anxiety and Panic Attacks
Ativan is highly effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and panic attacks. It works quickly, usually within 30 minutes to an hour, and produces a calming and relaxing effect that can last for several hours. Ativan is particularly useful for treating panic attacks, which are sudden and intense episodes of fear and anxiety that can cause physical symptoms such as palpitations, sweating, and shortness of breath. Ativan can help prevent panic attacks from occurring and reduce the severity of symptoms when they do occur.
Ativan and Xanax
Ativan and Xanax are both benzodiazepines that are commonly used to treat anxiety and panic disorders. While they have similar effects, there are some differences between the two drugs. Ativan has a longer half-life than Xanax, which means it stays in the body for a longer time and produces a more sustained effect. Ativan is also less potent than Xanax and has a lower risk of causing rebound anxiety or withdrawal symptoms. However, Ativan may be more likely to cause sedation and impair coordination compared to Xanax.
Ativan for Depression
Ativan is not a first-line treatment for depression, but it may be used as an adjunctive therapy for people who have not responded to other antidepressants. Ativan can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and agitation that often accompany depression, and it may also improve sleep and appetite. However, Ativan should be used with caution in people with depression, as it can worsen depressive symptoms and increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Taking Ativan While Starting Lexapro
Lexapro is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that is commonly used to treat depression and anxiety disorders. When starting Lexapro, some people may experience initial side effects such as anxiety, insomnia, or agitation. Ativan can be useful in managing these symptoms and reducing the risk of worsening anxiety or panic attacks. However, Ativan should only be used for a short period of time, as it can interfere with the effectiveness of Lexapro and increase the risk of side effects. It is important to discuss any concerns or questions about taking Ativan while starting Lexapro with your doctor.
Dosage of Ativan for MRI Claustrophobia
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a diagnostic test that uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce images of the body’s internal structures. Some people may experience anxiety or claustrophobia during an MRI, especially if they are required to remain still inside the narrow tube for an extended period. Ativan can be prescribed to help alleviate these symptoms and make the MRI experience more comfortable. The dosage of Ativan for MRI claustrophobia may vary depending on the individual’s anxiety level and medical history, but typically ranges from 0.5 mg to 2 mg taken 30 minutes to an hour before the procedure.
Ativan for Sleeping
Ativan can be used as a short-term treatment for insomnia, especially when other medications or non-pharmacological interventions have failed to produce significant improvement. Ativan can help improve sleep quality and duration, reduce sleep latency (the time it takes to fall asleep), and prevent nighttime awakenings. However, Ativan should only be used for a short period of time, as long-term use can lead to tolerance, dependence, and rebound insomnia. It is also important to avoid taking Ativan with alcohol or other sedative medications, as this can increase the risk of respiratory depression and other adverse effects.
Ativan for Flying and Flight Anxiety
Flying can be a stressful and anxiety-provoking experience for some people, especially if they have a fear of flying or a history of panic attacks. Ativan can be prescribed to help manage flight anxiety and make the flying experience more comfortable. The dosage of Ativan for flying may vary depending on the individual’s anxiety level and medical history, but typically ranges from 0.5 mg to 2 mg taken 30 minutes to an hour before the flight. It is important to discuss any concerns or questions about using Ativan for flying with your doctor, as it can interact with other medications or medical conditions.
Ativan Rebound Anxiety
Rebound anxiety is a common side effect that can occur when stopping Ativan abruptly or reducing the dosage too quickly. Rebound anxiety is characterized by a sudden onset of anxiety symptoms that are more severe than before starting the medication. Rebound anxiety can also occur if Ativan is used for a long period of time or at high doses. To minimize the risk of rebound anxiety, Ativan should be tapered gradually over several weeks under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Ativan for OCD
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition that is characterized by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) that are difficult to control. Ativan is not a first-line treatment for OCD, but it may be used as an adjunctive therapy for people who have not responded to other medications or psychotherapy. Ativan can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and agitation that often accompany OCD, but it is not a cure for the condition.
Ativan Dosage for Dental Anxiety
Dental anxiety is a common condition that affects many people and can make dental procedures challenging and uncomfortable. Ativan can be prescribed to help manage dental anxiety and make the dental experience more tolerable. The dosage of Ativan for dental anxiety may vary depending on the individual’s anxiety level and medical history, but typically ranges from 0.5 mg to 2 mg taken 30 minutes to an hour before the procedure.
Ativan and Depression
Ativan should be used with caution in people with depression, as it can worsen depressive symptoms and increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Ativan is not a first-line treatment for depression, but it may be used as an adjunctive therapy for people who have not responded to other antidepressants. Ativan can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and agitation that often accompany depression, but it is not a cure for the condition.
Conclusion
Ativan is a highly effective medication for treating anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia. It produces a calming and relaxing effect that can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. However, Ativan should only be used for a short period of time and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider. Long-term use of Ativan can lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and can cause serious side effects. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and not to exceed the recommended duration of treatment.
Comments are closed.